
They flow easily outward from the vent (where it comes out of the ground), and may travel great distances before completely solidifying.įelsic lavas are not as hot, high in silica and volatiles, and have a high viscosity. So, mafic lavas are hot, low in silica and volatiles, and have relatively low viscosity. So mafic/basaltic volcanoes are fairly quiescent, intermediate/andesitic volcanic eruptions are moderately explosive, and felsic/rhyolitic volcanoes may be extremely explosive. In general, the more felsic the magma the greater the volatile content. The escape of gases may produces tremendous force in a volcano, producing explosive eruptions. When lava approaches the surface, the pressure on it is greatly reduced and the dissolved gases come out of solution they form bubbles and rise. There is commonly also nitrogen, sulfur dioxide, and small amounts of chlorine, hydrogen, argon, and a few other gases. The two most abundant gases in lava are water vapor and carbon dioxide. Lavas may contain up to 6% or more of their mass as gases. Volatile content refers to gases dissolved in the lava, like carbon dioxide in soft drinks. Felsic lavas are low temperature lavas because lower temperatures are required to keep felsic minerals molten (and if it was hotter it would have incorporated more iron and magnesium in comparison to silica). It turns out that mafic lava is high temperature lava because high temperatures are required to melt mafic minerals in the first place. The more mafic the lava (the less silica in it), the lower the viscosity. The cooler the lava, the higher the viscosity (the thicker it is).Ĭomposition: he more felsic the lava (the more silica in the lava), the higher the viscosity because silica forms chains in the cooling lava even before it crystallizes. Temperature: The hotter the lava, the lower the viscosity (the thinner it is). Temperature, composition, and volatile (gas) content largely determine the viscosity of lava. Hot syrup becomes thinner, runnier, more like water. But when syrup is heated, its viscosity goes down. Cold syrup, on the other hand, has a higher viscosity. Water, for example, is a low viscosity fluid.
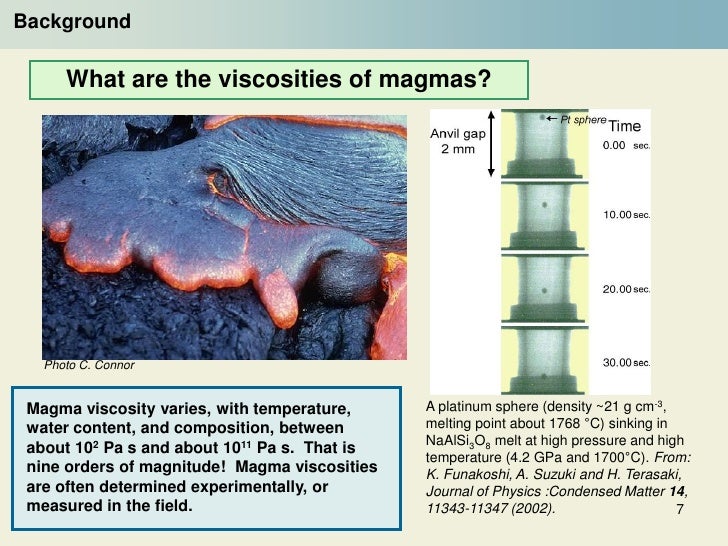
Viscosity is a fluid's resistance to flow.

The shape of a volcano is largely determined by the type of lava that has erupted, and importantly, its viscosity. The overall size of a volcano is determined by the total volume of lava that has erupted. Volcanoes come in different sizes and shapes.

Volcanoes are built by successive eruptions over many decades, centuries, or thousands of years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
